최근 들어 physical AI나 디지털 트윈에 대한 관심이 높은데, 이런 주제들에서 중요한 것이 시뮬레이션이다. 물리 시뮬레이션을 어떻게 할 것인가는 graphics에서도 많이 고민한 부분이라(특히 게임업계) 나중에 이에 대한 글도 쓰면 좋겠다.
기계공학과 비슷한 계열의 엔지니어링 관점에서 봤을 때는 differential equation를 적분하는 방식으로 시뮬레이션을 돌린다.
하지만 우리가 다루는 물리적 법칙이 어느 스케일까지 적용 가능한지에 따라 물리 법칙을 유도하고 시뮬레이션 돌리는 방식이 다를 수 있다는 것을 최근 들어 알게 되었다. (아직 공부중...)
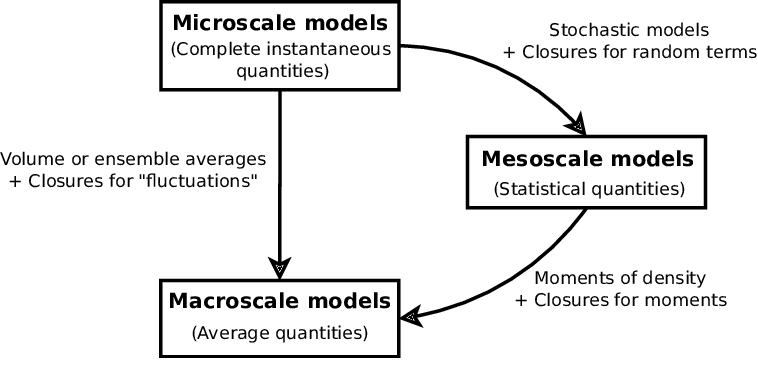
왜냐하면 이 글에서 다룰 Lattice Boltzmann method (이하 LBM)은 mesoscopic scale에서 evolving flow field를 표현한 것이기 때문이다.
최근에는 Lattice Boltzmann Method (kinetic gas theory)를 기반으로 한 시뮬레이션이 주목을 받고 있다.
Laminar, turbulent flow
Subsonic, supersonic flow
flow through porous media
free-surface and multiphase flows
등에 활용될 수 있다.
1. Lattice Boltzmann method
LBM equations은 velocity distribution function $f_i(x,t)$의 공간, 시간에 대한 행동을 묘사하는 time-dependent and discrete equatios으로 구성되어있다.

i : discrete lattice directions 인덱스를 의미한다.
여기서 $\mathcal{l]$는 general collision operator를 의미한다. 따라서 collison operator를 어떻게 정의하느냐에 따라 결과가 달라질 수 있다.
이 collison operator는
form of the moment space 기반 방법들
- Bhatnagar-Gross-Krook
- multi-relaxation time (MRT)
좀 더 발전된 방법들
- cumulant collision
- recursive regularized / multi-relaxation entropic model 등이 있다.
이 글에서는 Bhatnagar-Gross-Krook (BGK) method를 기반으로 한다.
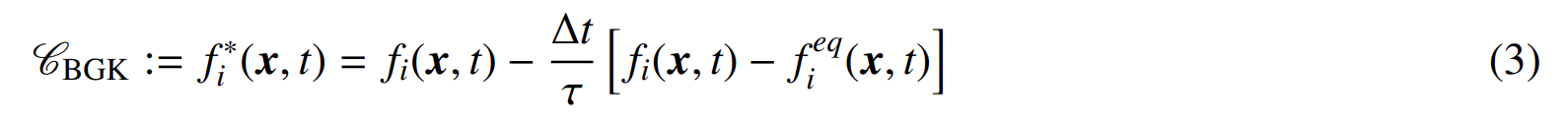
$f_i^{eq}$는 equilibrium state를 의미하고 time scale $\tau$는 다음과 같이 정의된다. $\Delta t$는 discrete time step:
$$\tau=\frac{\nu}{c_{s}^2}+\frac{\Delta t}{2}$$
$$c_s^2 = \frac{1}{3} \left(\frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}\right)^2$$
collision model과 별개로 equilibrium distribution function $f_i^{eq}$는 다음과 같이 계산된다.

$w_i$는 each lattice direction $c_i$과 관련된 weight이다. $\rho$는 fluid density, $u$는 velocity, $p$는 pressure는 macroscopic state variables로 다음과 같이 유도된다.

실제 implementation 할 때는 다음과 같은 lattices를 선택한 다음에,
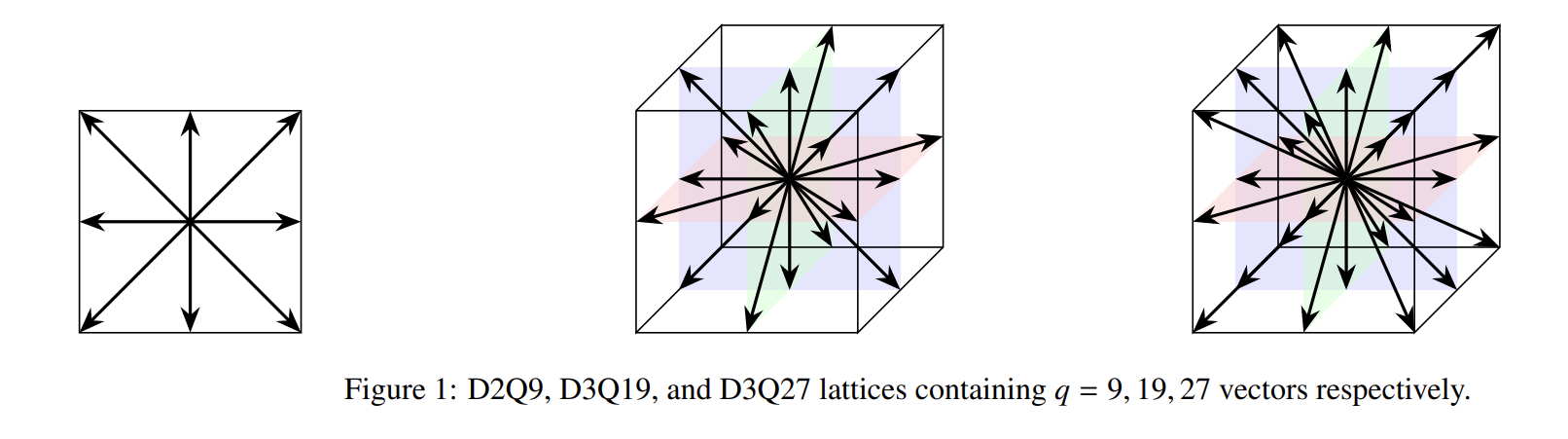
위의 collision operator를 적용하고, boundary condition을 적용한다. 그 다음에 streaming operation을 적용하고 boundary condition을 적용한다. collision operator와 streaming operation+boundary conditions이 포함된 이 프로세스를 한 스텝으로 생각할 수 있다. boundary condition 타입에 따라 collision 이후에 적용할지, streaming 이후에 적용할지가 결정된다. 이를 반복해서 풀면 된다.
더 디테일한 수식이나 implementation은 아래 마지막 참고 문헌을 보는 게 좋을 듯하다.
참고문헌
XLB: A Differentiable Massively Parallel Lattice Boltzmann Library in Python
This research introduces the XLB library, a scalable Python-based...
www.research.autodesk.com
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-44649-3_3
'수치해석 Numerical Analysis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [시뮬레이션] 미분가능 시뮬레이션 코드 (0) | 2026.01.17 |
|---|---|
| [수치해석] Partial Differential Equation (4) Modified Wavenumber Analysis (0) | 2025.07.20 |
| [수치해석] Partial Differential Equation (3) Von Neumann Stability Analysis (0) | 2025.07.20 |
| [수치해석] Partial Differential Equation (2) Matrix stability analysis (0) | 2025.07.20 |
| [수치해석] Partial Differential Equation (1) semi-discretization (0) | 2025.07.20 |