
보기 편하게


1. The Direct Method of Lyapunov
Direct method 말고도 indirect method도 있다고 합니다. 그 경우에는 Nonlinear system을 Linearization해서 stability를 구하는 방법이라고 들었는데, Nonlinear system, Hassan K Kalid 책에 나와있는 것을 본 적이 있어서, 나중에 그 책을 읽고 indirect method에 대해서 공부해보고 싶네요.
어쨌든, 지금까지 stability를 다루는 방식은 eigenvalue를 찾거나, routh-hurwitz 방법을 사용하는 것이었습니다. 하지만 eigenvalue와 routh-hurwitz는 LTI system이 아니라면 구할 수가 없다는 점이 있습니다.
그래서 이번에는 Linear/nonlinear time-invariant/time-varying system에 관계없이 적용할 수 있는 방법을 이야기하고자 합니다.
바로 Lyapunov function을 구해서 이 function의 definiteness를 확인하는 방법입니다.
Lyapunov function을 바로 들어가기에 앞서 예시를 보면서, Lyapunov function의 물리적 의미(항상 적용할 수 있는 것은 아니지만)에 대해서 이야기하겠습니다.
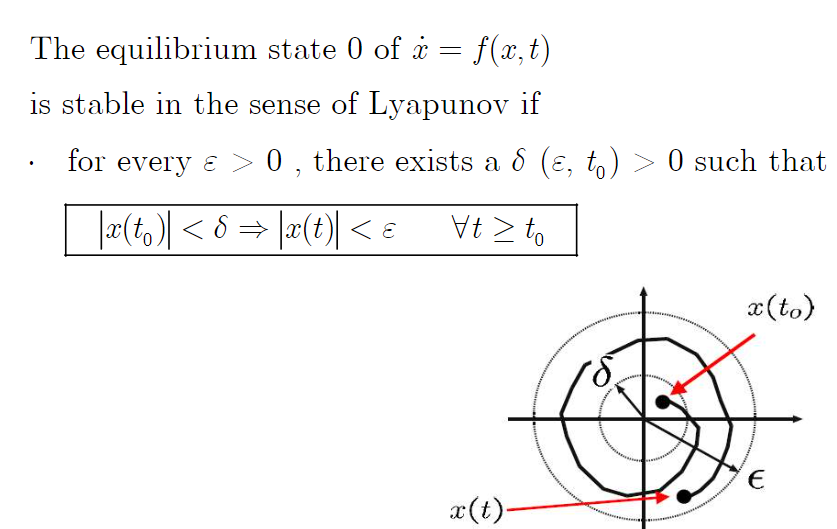
# 참고 : stability in the sense of Lyapunov
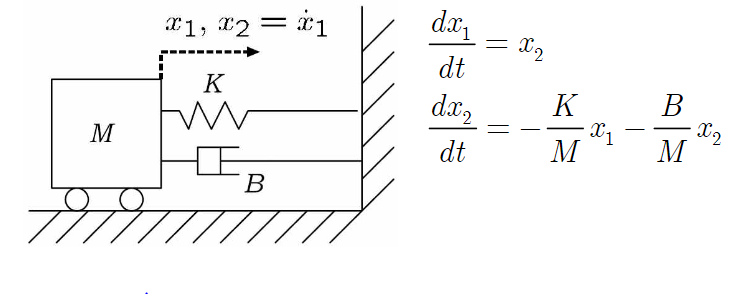
다음의 시스템에서 total energy를 구하면
$E(x,t)=\frac{1}{2}Kx_{1}^{2}(t)+\frac{1}{2}Mx_{2}^{2}(t)$ 입니다.
$\text{state }x=\begin{bmatrix} x_{1} & x_{2} \end{bmatrix}^{T}$
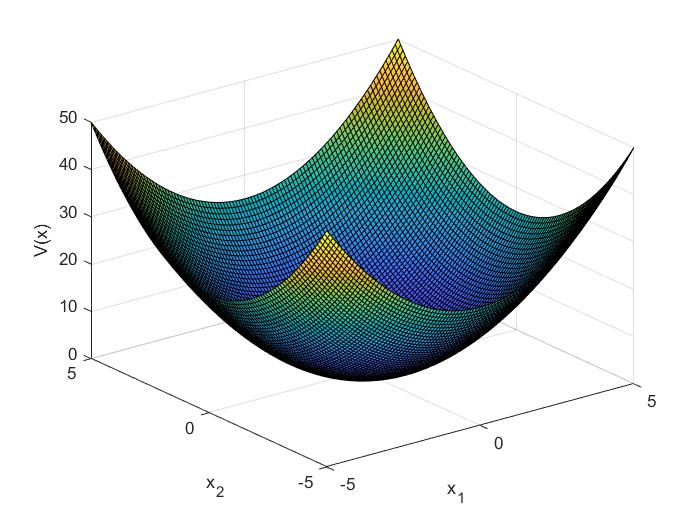
autonomous system이라고 생각해서 $E(x,t) \rightarrow E(x)$
$E(x)$는 위 그래프에 나온대로 positive definite입니다. x가 0일 때 빼고는 모두 positive값이기 때문입니다.
$E(0)=0$
또한 위 그래프를 보면 아무 위치에 공을 놓았을 때, 어떤 input도 없다면 어느 곳에서 시작하든 원점으로 굴러떨어질 것 같지 않나요? 아마도 이 시스템은 stable하지 않을까 짐작해볼 수 있습니다.
이 때, energy equation의 time derivative를 구해보면,
$\dot{E} = (Kx_{1}\dot{x_{2}}+Mx_{2}\dot{x_{2}})$
$\dot{x_{1}}=x_{2}$, $\dot{x_{2}}=-\frac{K}{M}x_{1}-\frac{B}{M}x_{2}$임을 equation of motion에서 알기 때문에 대입합니다.
$\dot{E}=Kx_{1}x_{2}+Mx_{2}(-\frac{K}{M}x_{1}-\frac{B}{M}x_{2})=-Bx_{2}^{2}\leq 0 \Rightarrow \text{negative semidefinite}$
E의 미분은 negative semidefinite임을 알았습니다. $x_{2}=0$일 때만 0입니다.
그런데 $\dot{E}$ 식에서 $x_{1}$ 항은 안 나왔는데 그렇다면, $x_{1}\neq 0$이어도 되는 것일까?
만약 $x_{2}=0, x_{1}\neq 0$일 때를 계산해보자.
$\dot{E}=0$이고 $\dot{x_{1}}=x_{2}=0$, $\dot{x_{2}}=-\frac{K}{M}x_{1}$입니다.
$x_{1}=c$라고 가정하면 $\dot{x_{2}}=-\frac{K}{M}c={c}'$이고 적분하면 $x_{2}={c}'t$가 됩니다.
그런데 원래 $x_{2}=0$이라고 가정을 했으므로 $x_{2}={c}'t$는 모순이 됩니다. 즉, $x_{2}$가 0인데 $x_{1}$이 0이 아닌 상황은 불가능합니다.
따라서 $\dot{E}=0$이기 위해서는 $x_{1}=0, x_{2}=0$이고 원점에서 equilibrium point입니다.
2. Lyapunov function
위에서 본 energy equation은 일종의 lyapunov function이라고 볼 수 있습니다. 시스템의 stability를 확인하고 싶다면, 그 시스템에 다음 조건을 만족하는 lyapunov function이 있는지 확인하면 됩니다. 앞서 본 시스템에서는 E(t)가 Lyapounov function이 됩니다. Lyapunov function의 형태가 정해진 것은 아니므로 그 시스템에서 찾을 수만 있으면 됩니다.
$\textbf{Lyapunov function : }$
$\text{A Locally Positive Definite Function(LPDF) V(x) is a Lyapunov function for the system}$
$\dot{x}=f(x) \cdots (1)$
$\text{if there exists a constant }r>0\text{ such that derivative of V(x) along the state trajectory (1) is }$
$\dot{V}(x)=\nabla W^{T}(x)f(x)\leq0\text{ for all }|x|<r$
(derivative of V(x) along the state trajectory에 대한 식은 맨 아래에 있습니다.)
조금 복잡해보이지만 요약하면, Lyapunov function $V(x)$는 Locally positive definite function이면서, state trajectory에 따른 derivative 값은 Locally negative semi-definite이어야합니다.
참고로 Locally positive definite보다 positvie definite이 더 까다로운 조건이므로, $V(x)>0$ (positive definite), $\dot{V(x)}<0$(negative definite) 여도 lyapunov function입니다.
$\textbf{Theorem 1}$
$\text{The equilibrium point 0 for the system }\dot{x}=f(t,x)\text{ at time }t_{0}$
$\text{ is stable in the sense of Lyapunov if there exists a LPDF V(t,x) such that}$
$\dot{V}(t,x)\leq 0$
$\text{for all }t\geq t_{0}\text{ and all }x\text{ such that }|x|<r\text{ for some }r>0$
즉 어떤 시스템 $\dot{x}=f(x)$에서 lyapunov function이 존재한다면 그 시스템은 equilibrium point에서 stable in the sense of Lyapunov입니다.
$\textbf{Theorem 2}$
$\text{The equilibrium point 0 for the system }\dot{x}=f(t,x)\text{ at time }t_{0}$
$\text{ is uniformly stable in the sense of Lyapunov over }[t_{0},\infty]\text{ if there exists a decrescent LPDF V(t,x) such that}$
$\dot{V}(t,x)\leq 0$
$\text{for all }t\geq t_{0}\text{ and all }x\text{ such that }|x|<r\text{ for some }r>0$
$\textbf{Theorem 3}$
$\text{The equilibrium point 0 for the system }\dot{x}=f(t,x)\text{ at time }t_{0}$
$\text{ is globally asymptotically stable over }[t_{0},\infty]\text{ if there exists a radially unbounded LPDF V(t,x) such that}$
$\dot{V}(t,x)\leq -\gamma(|x|)$
$\text{for all }t\geq t_{0}\text{ and all }x\in\mathbb{R}^{n}\text{, where }\gamma:\mathbb{R}_{+}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}_{+}\text{ is a K-class function}$
radially unbounded는 globally에 대한 근거이고,
$\dot{V}(t,x)\leq -\gamma(|x|)$는 asympotitcally에 대한 근거이다.
위의 내용은 non-autonomous system에 대한 내용이었고, 지금은 autonomous system에 대한 theorem입니다.
$\textbf{Theorem 4}$
$\text{The equilibrium state 0 of n-th order nonlinear time-invariant continous time system }\dot{x}=f(x)$
$\text{ is locally asymptotically stable if there exists a LPDF Lyapunov function V(x) such that}$
$\dot{V}(x)<0$
$\text{for all }0<|x|<r\text{ for some }r>0$
즉, $V(x), -\dot{V}(x)$ 둘 다 LPDF인 경우.
만약에 $\dot{V}(x)\leq 0$이었더라면(negative semidefinite)라면 stable in the sense of Lyapunov입니다.
(원점에 도달하기 전에 다른 평형 state에서 멈춰도 괜찮은 경우)
$\textbf{Theorem 5}$
$\text{The equilibrium state 0 of n-th order nonlinear time-invariant continous time system }\dot{x}=f(x)$
$\text{ is globally asymptotically stable if there exists a PDF Lyapunov function V(x) such that}$
$\dot{V}(x)<0 \forall x\in R$
$V(x), -\dot{V}(x)$ 둘 다 PDF인 경우에는 globally asymptotically stable.
$\textbf{LaSalle's Asymptotic stability Theorem : }$
$\text{The equilibrium state 0 of }\dot{x}=f(x)\cdots (1)$
$\text{ is locally asymptotically stable if there exists a LPDF V(x) such that, for some }r>0$
1) $\dot{V}(x)\leq0 \forall |x|<r$
2) $\text{The set S}={x:V(x)\leq m, dot{V}(x)=0}$
$\text{contains no trajectories of (1) other than }x=0\text{, where }m=undetset{|x|\leq r}{sup}V(x)$
$sup$ : supremum 상한
위에 좀 복잡하게 적혀있지만 사실 상 바로 위에 있는 theorem 4와 별반 다르지 않다. $x=0$일 때를 빼고는 $\dot{V}(x)=0$이어서는 안된다는 의미입니다. locally asymptotically stable이라는 것이 특정 범위 안에서 서서히 원점으로 다가가야하므로, 중간에 $V(x)$가 멈추는 곳이 있으면 안된다는 것입니다.
(Lyapunov function이 dynamic system에서 에너지의 의미로 많이 쓰이니, 어떤 0이 아닌 state에서 에너지가 0이면 그대로 멈춰버리니, 원점으로 수렴할 수 없으므로 그래서는 안된다는 의미로 해석해도 좋습니다.)
$\textbf{Instability Theorem}$
$\text{The equilibrium state 0 of : }\dot{x}=f(x)$
$\text{ is unstable if there exists a LPDF W(x) such that}$
$\dot{W}(x)>0 \text{ for all }0<|x|<r \Rightarrow \dot{W}(x)\text{ is a LPDF}$
autonomous system에 대해서 정리하면
# Derivative along a state trajectory
$x\in \mathbb{R}^{n}$에 대한 함수 $W : \mathbb{R}^{n}\rightarrow \mathbb{R}_{+}$가 있을 때, 시간에 따른 $W(x)$의 변화(derivative, $\frac{W(x)}{dt}$는 state trajectory와 연관이 있습니다.
nth order nonlinear time invariant continous time system : $\dot{x}=f(x)\text{, where }f(0)=0$
또한 gradient of W $\nabla W(x)=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial W}{\partial x_{1}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial W}{\partial x_{n}}\end{bmatrix}^{T}$ 입니다.
derivative of $W(x)$ along the state trajectory $\dot{x}=f(x)$는
$\frac{dW(x)}{dt}=\nabla W^{T}(x)\frac{dx}{dt}=\nabla W^{T}(x)f(x)=\begin{bmatrix}\frac{\partial W}{\partial x_{1}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial W}{\partial x_{n}}\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} f_{1}(x) \\ \vdots \\ f_{n}(t) \end{bmatrix}$
이와 같은 $\nabla W^{T}(x)f(x)$를 $\textbf{Lie derivative of W(x) with respect to the vector field f(x)}$ 라고 합니다.
$L_{f}W(x)=\nabla W^{T}(x)f(x)$
다음에는 LTI system에서 Lyapunov equation과 그 solution에 대해 다뤄보겠습니다.
'연구 Research > 제어 Control' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov's Direct Method (5) - Solving Lyapunov equation (0) | 2021.01.24 |
|---|---|
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov's Direct Method (4) - Lyapunov equation (0) | 2021.01.24 |
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov's Direct Method (2) - Quadratic function (0) | 2021.01.23 |
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov Direct Method (1) - Positive definite (0) | 2021.01.22 |
| [고등자동제어] Stability in the sense of Lyapunov (3) (0) | 2021.01.15 |