
이제 LTI system에서 Lyapunov function을 구하는 과정에 대해서 공부하겠습니다.
1. Lyapunov stability theorem
그 전까지는 nonlinear system도 포함하기 위해 $\dot{x}=f(x)$라는 state trajectory를 사용했습니다. (autonomous system) 또한 이 시스템에서 lyapunov function을 찾으면 stable in the sense of Lyapunov임을 알았습니다.

(자세한 내용은 normal-engineer.tistory.com/51)
이제는 LTI system에서 Lyapunov function을 다뤄보겠습니다.
nth order LTI system
$\dot{x}=Ax$
이 있을 때
nonlinear system에 적용했던 것과 동일하게(아래 그림 참고) lyapunov stability theorem을 적용하면
$\textbf{Theorem 1 : Lyapunov's Stability Theorem}$
$\text{The origin 0 of the nth order LTI system }\dot{x}=Ax$
$\text{is stable in the sense of Lyapunov if there exists a LPDF V(x) such tat, for some }r>0$
$\dot{V}(x)=\nabla V^{T}Ax \leq 0$ $\forall |x|<r \text{ (recall Lie derivative)}$
$\Rightarrow\text{ There exists a Lyapunov function V(x) for this system.}$
nth order LTI system에서 lyapunov function이 존재하면 이 시스템은 stable in the sense of Lyapunov.
또한 만약 $\dot{V}(x)=\nabla V^{T}(x)Ax<0\text{, }\forall x\neq0$
이면 이 시스템은 asymptotically stable입니다.
2. Lyapunov equation
1) $\dot{V}(x)=\nabla V^{T}Ax$
이전에 quadratic function에 대해서 공부한 이유가 이제 여기서 나옵니다.
우리는 system의 stability를 판정하기 위해 Lyapunov function을 찾고 싶은 상황이라고 해봅시다. 이 때 Lyapunov function의 적절한 후보자가 있는데 바로, quadratic function입니다.
$V(x)=x^{T}Px\text{, }P^{T}=P\text{, }P>0\rightarrow\text{ P is positive definite}$
Lyapunov function의 후보 중 하나로 quadratic function을 고릅니다. 이 때 P는 어떤 symmetric positive definite이라고 하겠습니다.
이 때 $\dot{V}(x)$를 구하면 $x^{T}[A^{T}P+PA]x$로 구할 수 있습니다.
# $\dot{V}(x)=x^{T}[A^{T}P+PA]x$ 구하는 방법
- 바로 $V(x)$를 미분
$V(x)=x^{T}Px$일 때 ($P^{T}=P$, $P>0$)
$\dot{V}(x)=dot{x}^{T}Px+x^{T}Px=x^{T}A^{T}Px+x^{T}PAx (\because (\dot{x})^{T}=(Ax)^{T}=x^{T}A^{T})$
$=x^{T}\{A^{T}P+PA\}x$
- $\nabla V^{T}Ax$를 구해서 $\dot{V}(x)$를 구하는 방법
$P = \begin{bmatrix}p_{1} & p_{2} & \cdots & p_{n}\end{bmatrix}$
라고 할 때
$V(x)=\sum_{j=1}^{n}(x^{T}p_{j})x_{j}$ (아래 그림 참고하면 이해하는데 도움됩니다.)
$\frac{\partial V(x)}{\partial x_{i}}=2\sum_{j=1}^{n}\frac{\partial x_{j}}{\partial x_{i}}=2x^{T}p_{i}$
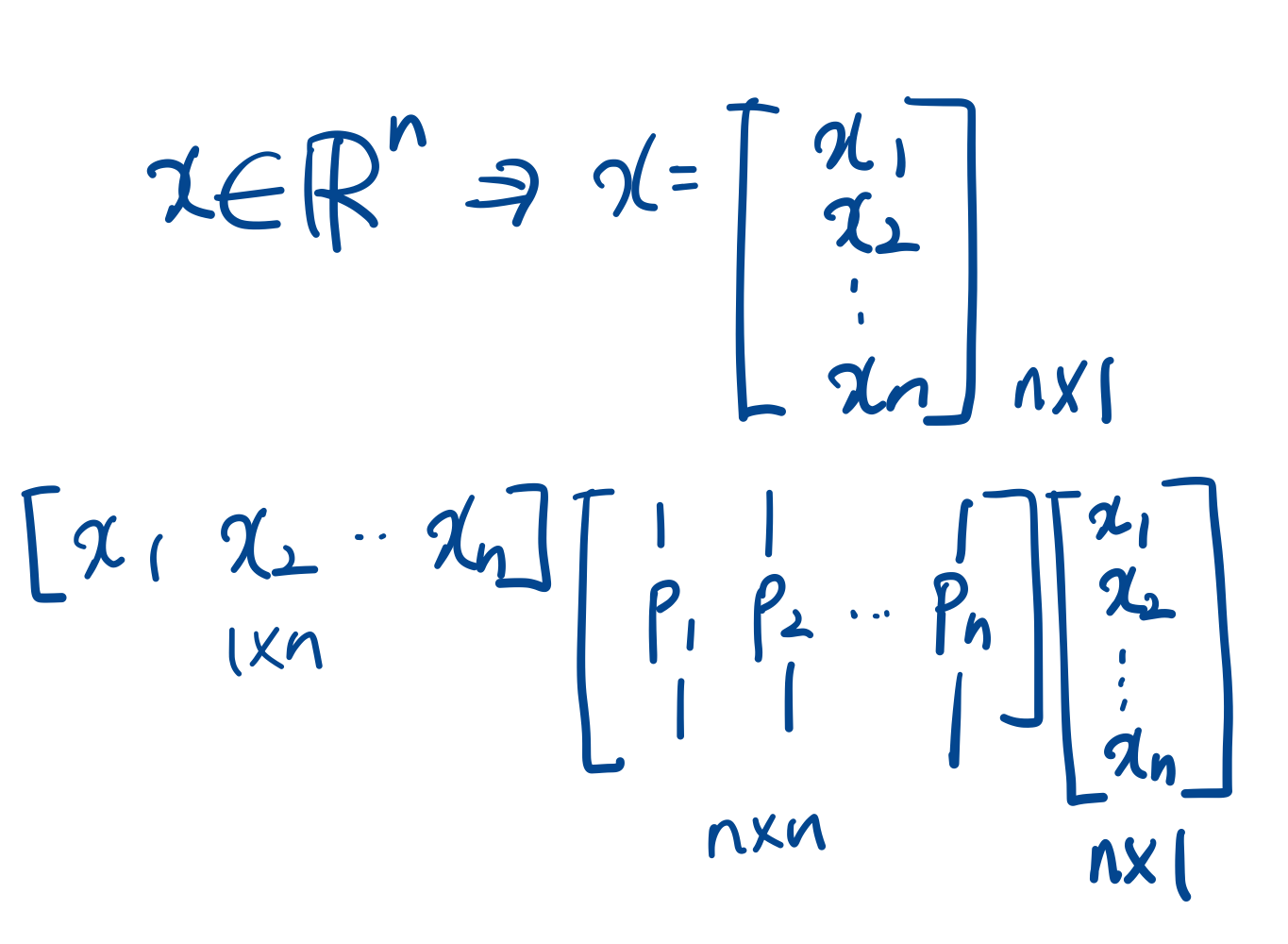
$\nabla V^{T}Ax=\begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial V(x)}{\partial x_{1}} & \cdots & \frac{\partial V(x)}{\partial x_{n}}\end{bmatrix}=2x^{T}P$
$\dot{V}(x)=\nabla V^{T}(x)\dot{x}=\nabla V^{T}(x)Ax=2x^{T}PAx=x^{T}{A^{T}P+PA}x$
$\because 2x^{T}PAx=x^{T}PAx+x^{T}PAx=(x^{T}PAx)^{T}+x^{T}PAx=x^{T}(A^{T}P+PA)x$
$x^{T}PAx$가 1 by 1 matrix이기 때문에 가능한 것입니다.
이 때, Lyapunov's stability theorem(이 글의 Theorem 1)를 보면 $P$는 positive definite이고,
$[A^{T}P+PA]\leq0$, 즉 negative semidefinite일 때 stable in the sense of Lyapunov입니다.
negative definite이면 asymptotically stable입니다.
그런데 여기서 문제는, $P$가 positive definite이면서, $[A^{T}P+PA]$가 negative definite인 P를 찾을 수 있느냐는 것입니다.
그래서 여기서 Lyapunov equation 문제가 나옵니다.
2) Lyapunov equation
$\textbf{Lyapunov equation : }A^{T}P+PA=-Q$
다음과 같이 -Q를 설정한 다음, 임의의 positive semidefinite Q에 대하여 P가 존재하는지, equation을 푸는 것입니다.
$\textbf{Theorem 2 - Lyapunov equation}$
$\text{The origin 0 of the nth order LTI system }\dot{x}=Ax$
$\text{is globally stable if and only if,}$
$\text{for any positive definite symmetric matrix Q, }$
$\text{there exist a positive definite symmetric matrix P, which is the unique solution of the Lyapunov equation}$
$A^{T}P+PA=-Q$
복잡해보이지만 간단하게 말하면, 어떤 PD symmetric matrix Q에 대하여 Lyapunov equation의 solution으로 PD symmetric matrix P가 존재할 때 이 시스템이 globally stable합니다.
(matrix에 대해서는 Locally Positive definite가 불가능해서 이렇게 된 것으로 보입니다.)
여기서 주목할 점
위의 equation에서 구한 P를 가지고 $V(x)=x^{T}Px$를 구하면 이 $V(x)$가 Lyapunov function입니다.
P가 positive definite라고 해서 Q가 positive definite인 것은 아니다. 하지만 A가 stable matrix라면 Q가 positive definite라면 P는 positive definite입니다.
그리고 꼭 $x$가 모두 real elements를 가진다는 보장은 없기 때문에 다음과 같은 theorem 2의 variation도 성립합니다.
$\textbf{Theorem 3 - considering complex domain}$
$\text{All the eigenvalues of A have negative real parts, or equivalently,}$
$\text{The 0 state of the nth order LTI system }\dot{x}=Ax$
$\text{is asymptotically stable if and only if,}$
$\text{for any positive definite}\textbf{ hermitian}\text{ matrix Q, }$
$\text{there exist a positive definite hermitian matrix P, which is the unique solution of the Lyapunov equation}$
$A^{T}P+PA=-Q$
3. Stability analysis
이제 위의 theorem을 통해, lyapunov equation을 풀어서 stability를 분석할 수 있다는 것을 알았을 것입니다. (강조하지만 지금은 LTI system을 다루고 있습니다. LTI system이어야 Lyapunov equation을 가질 수 있으니까요.)

stability analysis를 도식화하면 다음과 같습니다.
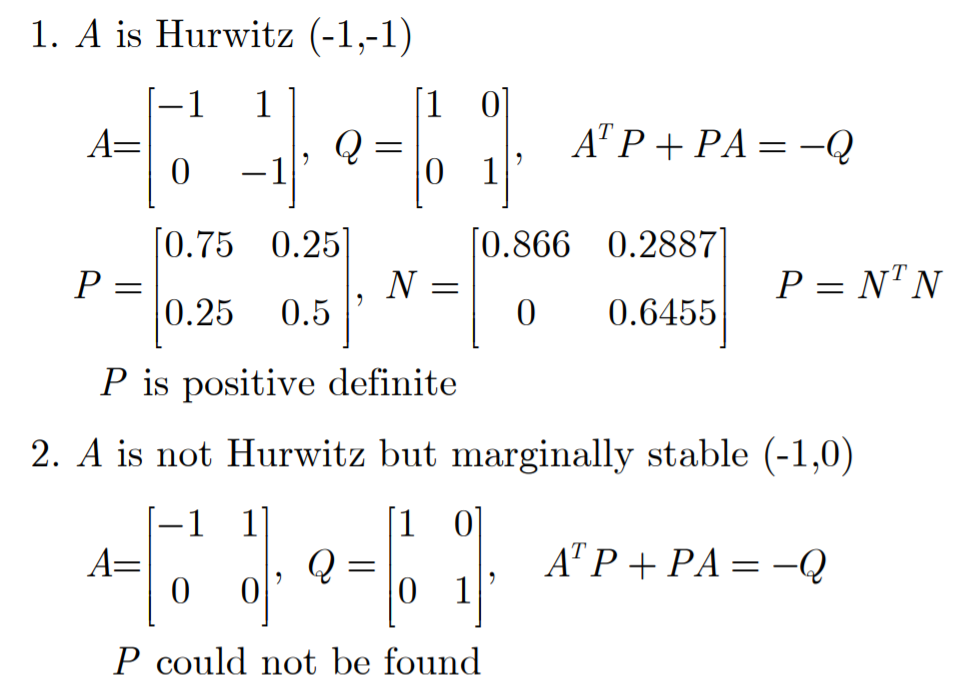
일단 lyapunov equation을 풀어서 P가 존재하는지 확인합니다.
P가 존재하지 않는다는 것은, A가 Hurwitz가 아니라는 것을 의미하고, 이는 두 가지 경우가 있는데 unstable한 경우와 marginal stable한 경우입니다.
P가 존재한다면, P가 positivie definite인지 아닌지 확인합니다.
P가 PD이면, A는 Hurwitz입니다.
또 P가 PD가 아니면, A는 unstable입니다. (marginal stable은 아님)
예시를 통해서 살펴보겠습니다.

마지막으로는 Lyapunov equation을 선형방정식에 대한 지식을 통해 푸는 방법에 대해서 다루겠습니다.
'연구 Research > 제어 Control' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [제어] Dynamic programming - Richard Bellman (0) | 2021.02.10 |
|---|---|
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov's Direct Method (5) - Solving Lyapunov equation (0) | 2021.01.24 |
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov's Direct Method (3) - Lyapunov function (0) | 2021.01.23 |
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov's Direct Method (2) - Quadratic function (0) | 2021.01.23 |
| [고등자동제어] Lyapunov Direct Method (1) - Positive definite (0) | 2021.01.22 |