응용선형대수에서 굉장히 중요한 개념인 Four fundamental subspaces
Ax=b에서 b가 A의 matrix의 column space 안에 속해야 solution이 존재한다고 이야기했었고, null space 속한 vector를 더해도 Ax의 값에 영향을 미치지 못하므로 solution에 null space vector를 더한 것 역시 solution이 될 수 있었습니다.
$A\bar{x}=b$인 $\bar{x}$는 solution입니다. 이 때 null space에 속한 벡터 $\tilde{x}(\Rightarrow A\tilde{x}=0)$가 있을 때 $\bar{x}+\tilde{x}$도 solution이 됩니다.
$A(\bar{x}+\tilde{x})=A\bar{x}+A\tilde{x}=b$
$\text{Given A }m\times n \text{matrix}$
$\text{1. Column space(Range space) : } C(A) \rightarrow \text{ a spanning space of all columns of A}$
$\text{2. Null space : } N(A) \rightarrow \text{ a spanning space of vector satisfying }Ax=0$
$\text{3. Row space : } C(A^{T}) \rightarrow \text{ a spanning space of all rows of A}$
$\text{4. Left null space : }N(A^{T}) \rightarrow \text{ a spanning space of vectors satisfying }A^{T}y=0$
각 space의 특징들에 대해서 설명하겠습니다.
3. Row space $C(A^{T})$
Row space of A = row space of u(echelon form) = row space of R(Reduced echelon form)
(A,u,R을 각 열의 선형 조합으로 구할 수 있으므로 A,u,R의 row space는 동일합니다. 주의해야할 점은 echelon form을 구할 때 $A^{T}$로 바꾸어서 만든 echelon form이 아니라 $A$에서 만든 echelon form이라는 점입니다.)
예시)
$A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 3 & 3 & 2\\ 2 & 6 & 9 & 7\\ -1 & -3 & 3 & 4\end{bmatrix}$
$u=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 3 & 3 & 2\\ 0 & 0 & 3 & 3\\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0\end{bmatrix}$
basis는 $\begin{bmatrix}1 & 3 & 3 & 2\end{bmatrix},\begin{bmatrix}0 & 0 & 3 & 3\end{bmatrix}$ 두 개입니다.
만약 $A^{T}=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & -1\\ 3 & 6 & -3\\ 3 & 9 & 3\\ 2 & 7 & 4\end{bmatrix}$
$A^{T}$로 구한 $u=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & -1\\ 0 & 3 & 6\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0\end{bmatrix}$의 column을 basis로 사용할 수 없습니다.
$A:m\times n$
$\dim (C(A^{T}))=r=\dim (C(A))$
$\text{rank }A = \text{rank }A^{T}$
$\begin{bmatrix}* & \cdots & & \\ & * & \cdots & \\ & & * & \end{bmatrix}$
A matrix를 echelon form으로 만들었을 때 row의 관점에서 보나, column의 관점에서 보나 pivot의 갯수는 동일하므로, $A$와 $A^{T}$의 rank가 같습니다.
A가 Square matrix라면, column vector가 linearly independent하다는 말은 곧 row vector가 linearly independent하다는 말과 동치입니다.
2. Null space $N(A)$
$Ax=0 \Leftrightarrow ux=0 \Leftrightarrow Rx=0$
$A \in \mathbb{R}^(m \times n)$
$\dim N(A)=n-r \text{(r : number of pivots, n-r : number of free variables)}$
$=\dim(\mathbb{R}^{n}-\text{rank }A)$
자세한 내용은 normal-engineer.tistory.com/74
[응용선형대수] Understanding Ax=0, Ax=b using null space matrix
1. Ax=b와 Column space&Null space 관계 이 column space와 null space 개념을 통해 $Ax=b$에 대해 이해해볼 수 있습니다. $\text{Given }Ax=b$ $\text{(i). C(A) provides information whether it has a solutio..
normal-engineer.tistory.com
1. Column space $C(A)$
$\text{basis for }C(u) \neq \text{basis for }C(A)$
4. Left null space $N(A^{T})$
$N(A^{T})=\{y:A^{T}y=0\}$
$\dim (N(A^{T}))=m-\text{rank}(A^{T})=m-r$
$\mathbb{R}^{n} \overset{A}{\underset{A^{T}}{\rightleftharpoons}} \mathbb{R}^{m}$
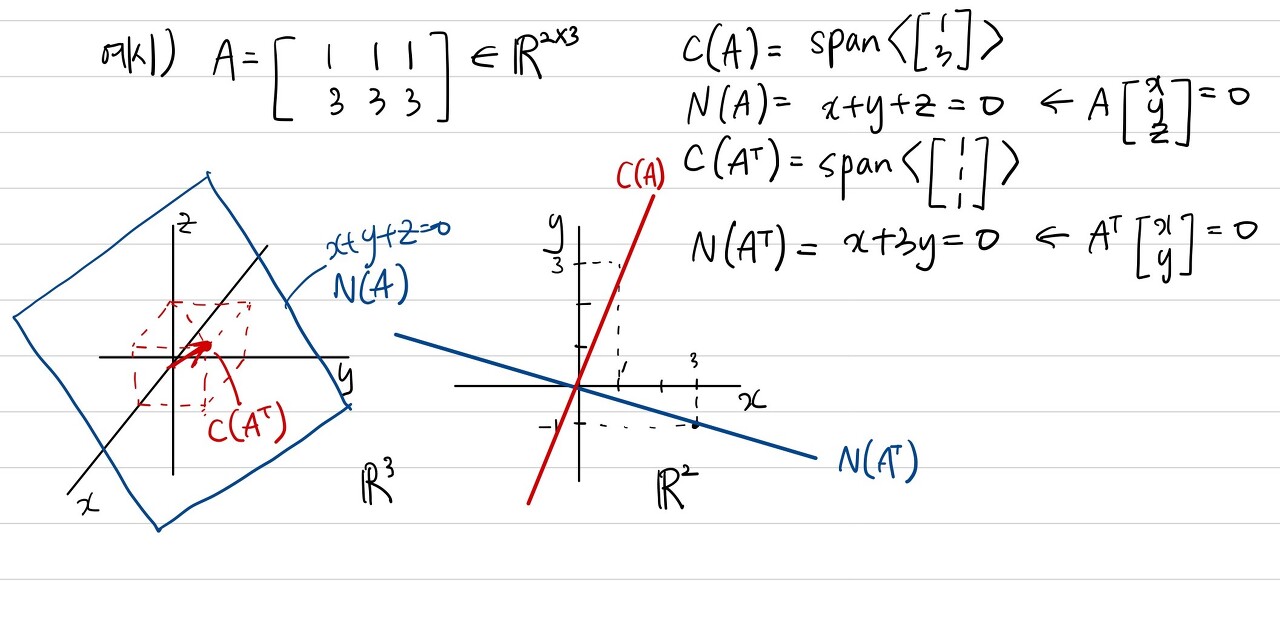
$A : m\times n$
$0\leq \text{rank }A\leq m,n$
$\text{rank }A=0 \Rightarrow A=0$
$(1). A:n\times n$
$\text{rank }A=n$
$\dim N(A)=0 \Leftrightarrow N(A)={0} \Leftrightarrow \text{A is invertible}$
$(2). A:m\times n$
$r=\text{rank }A=m\leq n$
$\text{right inverse exists }AC=I$
$C=A^{T}(AA^{T})^{-1}$
$\text{ex) }A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{bmatrix}$
$Ax=b \rightarrow$ 적어도 한 개의 solution 존재합니다.
$(3). A:m\times n$
$r=\text{rank }A=n\leq m$
$\text{left inverse exists }BA=I$
$B=(A^{T}A)^{-1}A^{T}$
$A=\begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & 0\end{bmatrix}$
$Ax=b \rightarrow$ 많아도 한 개의 solution
'수학 Mathematics > 선형대수학 Linear Algebra' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [응용선형대수] Orthogonal vectors and subspace (0) | 2021.03.06 |
|---|---|
| [응용선형대수] Linear Transformations (0) | 2021.03.05 |
| [응용선형대수] Linear independence, basis and dimensions (0) | 2021.03.02 |
| [응용선형대수] Understanding Ax=0, Ax=b using null space matrix (0) | 2021.02.25 |
| [응용선형대수] Null space/Column space (0) | 2021.02.25 |